OK Radar: A Comprehensive Guide
Have you ever wondered what radar is and how it works? Radar, short for Radio Detection And Ranging, is a technology that has become an integral part of our lives, from military applications to everyday consumer products. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of radar, exploring its history, components, applications, and future developments.
Understanding Radar

Radar is a system that uses electromagnetic waves to detect and locate objects. It works by emitting radio waves and analyzing the reflections that bounce back from objects in its path. By measuring the time it takes for the waves to return, radar can determine the distance to the object. Additionally, the angle at which the waves are reflected can be used to determine the object’s direction.
The basic principle of radar is quite simple. A radar system consists of a transmitter, which emits radio waves, and a receiver, which detects the reflected waves. The distance to the object is calculated based on the time it takes for the waves to travel to the object and back. The direction of the object is determined by the angle at which the waves are reflected.
Components of a Radar System

A radar system is composed of several key components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Transmitter | Generates and emits radio waves. |
| Antenna | Transmits and receives radio waves. |
| Receiver | Detects and processes the reflected radio waves. |
| Signal Processor | Analyzes the received signals to determine the distance, direction, and speed of the object. |
| Display | Displays the information about the detected object. |
These components work together to provide a comprehensive picture of the environment, allowing radar systems to be used in a wide range of applications.
Applications of Radar
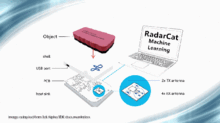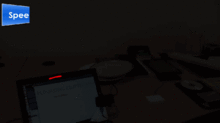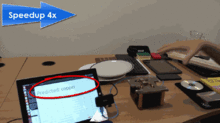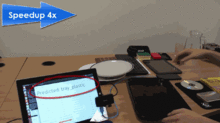
Radar technology has a wide range of applications, from military to civilian uses. Here are some of the most common applications:
- Military: Radar is used for air and sea surveillance, target tracking, and missile guidance.
- Aerospace: Radar is used for weather forecasting, air traffic control, and navigation.
- Automotive: Radar is used in advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) for collision avoidance, adaptive cruise control, and lane departure warning.
- Transportation: Radar is used for traffic monitoring, speed enforcement, and weather detection.
- Maritime: Radar is used for ship navigation, collision avoidance, and search and rescue operations.
Future Developments
The field of radar technology is constantly evolving, with new advancements being made all the time. Some of the most promising future developments include:
- Higher Frequencies: As technology advances, radar systems are being developed that operate at higher frequencies, allowing for greater resolution and accuracy.
- Multi-Functionality: New radar systems are being designed to perform multiple tasks simultaneously, such as detecting objects, measuring their speed, and tracking their movement.
- Integration with AI: The integration of radar technology with artificial intelligence is expected to revolutionize the way radar systems are used, making them more efficient and reliable.
Radar technology has come a long way since its inception, and it continues to play a crucial role in our lives. As technology advances, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of radar in the years to come.











