OKB of Formic Acid: A Comprehensive Overview
Formic acid, a simple organic compound with the chemical formula HCOOH, is a colorless, corrosive liquid that is naturally produced by ants and certain other insects. It is also found in some plants and is produced industrially for various applications. In this article, we delve into the various aspects of formic acid, including its properties, production, uses, and environmental impact.
Properties of Formic Acid
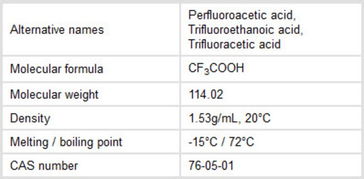
Formic acid is a weak organic acid that is soluble in water, alcohol, and ether. It has a pungent, acrid odor and is corrosive to metals and skin. The melting point of formic acid is -8.4掳C, and its boiling point is 100.2掳C. It is a colorless liquid at room temperature, but it can turn into a white solid when it is frozen.
Formic acid is a reducing agent and can be oxidized to carbon dioxide and water. It is also a weak acid, with a pKa value of 3.75. This means that it can donate a proton (H+) to a base, making it a weak acid in aqueous solutions.
Production of Formic Acid
Formic acid is produced industrially through several methods, including the oxidation of methanol, the hydrolysis of carbon monoxide, and the fermentation of glucose. The most common method is the oxidation of methanol, which is carried out in the presence of a catalyst, such as silver or copper, and oxygen.
The chemical equation for the oxidation of methanol to formic acid is:
| Reactants | Products |
|---|---|
| CH3OH + 1/2 O2 | HCOOH + H2O |
This process is highly exothermic and requires careful control of temperature and pressure to ensure the safety and efficiency of the reaction.
Uses of Formic Acid

Formic acid has a wide range of applications due to its unique properties. Some of the most common uses include:
-
Preservation: Formic acid is used as a preservative in food and beverages to prevent spoilage and extend shelf life.
-
Textile Industry: It is used in the textile industry to improve the dyeing process and to prevent the growth of bacteria and fungi.
-
Leather Industry: Formic acid is used in the leather industry to clean and preserve leather goods.
-
Chemical Synthesis: It is used in the synthesis of various chemicals, including esters, aldehydes, and ketones.
-
Medical Applications: Formic acid is used in some medical applications, such as the treatment of warts and corns.
Environmental Impact
While formic acid has many beneficial uses, it also has some environmental concerns. The production of formic acid releases carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change. Additionally, the release of formic acid into water bodies can be harmful to aquatic life.
However, the environmental impact of formic acid can be minimized through the use of renewable energy sources for production and the implementation of proper waste management practices.
Conclusion
Formic acid is a versatile and valuable compound with a wide range of applications. Its unique properties make it an essential ingredient in various industries. However, it is important to be aware of its environmental impact and to take steps to minimize any negative effects. By understanding the properties, production, uses, and environmental impact of formic acid, we can make informed decisions about its use and disposal.














